Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), a prevalent and potentially life-threatening condition, demands a comprehensive understanding to navigate its complexities. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into Congestive Heart Failure, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and the essential steps for living with this condition.
Understanding Congestive Heart Failure:
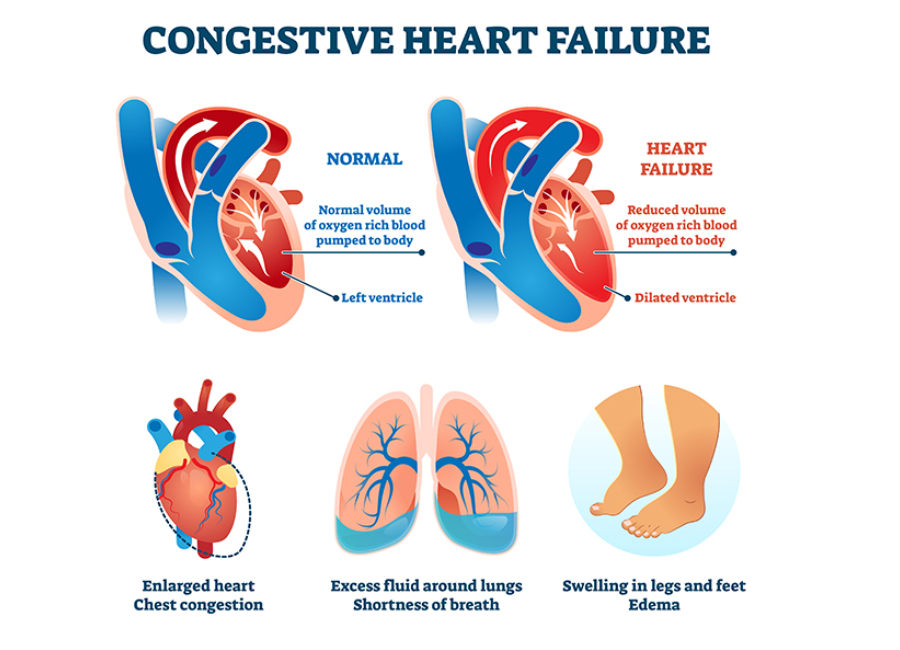
Congestive Heart Failure is a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, leading to an inadequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues. This results in the pooling of blood in the heart and a backup of fluid in the lungs and other parts of the body.
Causes of Congestive Heart Failure:
CHF can be caused by various factors, including:
- Coronary Artery Disease: Blockages in the coronary arteries can reduce blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to heart failure.
- High Blood Pressure: Chronic hypertension can strain the heart, causing it to weaken over time.
- Cardiomyopathy: Conditions that damage the heart muscle can lead to CHF.
- Heart Valve Problems: Issues with heart valves can disrupt blood flow and cause heart failure.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Some individuals are born with structural heart problems that can lead to CHF.
- Heart Attacks: A heart attack can damage the heart muscle and result in heart failure.
Common Symptoms of CHF:
Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure may include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or while lying flat.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet (edema).
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- Persistent cough or wheezing.
- Increased need to urinate at night.
- Diagnosis and Evaluation:
The diagnosis of CHF typically involves:
- Medical history and physical examination.
- Blood tests.
- Chest X-ray.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG).
- Echocardiogram.
- Cardiac catheterization.
- Treatment Options:
Treatment for CHF aims to relieve symptoms, improve heart function, and address underlying causes. It may include:
Medications: Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and other drugs can help manage symptoms and improve heart function.
Lifestyle Changes: Dietary modifications, salt restriction, regular exercise, and weight management are essential for heart failure management.
Surgery or Procedures: In some cases, heart surgeries or procedures like angioplasty or stent placement may be necessary.
Implantable Devices: Devices like pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) can help manage heart rhythm and function.
Living with CHF:
Living with Congestive Heart Failure requires commitment to medication, lifestyle changes, and regular medical monitoring. Patients are often advised to:
- Monitor their weight and symptoms.
- Follow a heart-healthy diet.
- Manage fluid and salt intake.
- Engage in regular, low-intensity exercise.
- Attend follow-up appointments with healthcare providers.
A deep dive into Congestive Heart Failure reveals the importance of awareness, early diagnosis, and comprehensive care. With the right treatment, lifestyle changes, and support, individuals living with CHF can manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Education and understanding are key, both for those affected by CHF and their loved ones, to navigate this challenging but manageable condition.